
Thus, not a single one of the radio-elements, known at the commencement of the year, has a peculiar chemical nature unshared by others. Radioactinium was shown to be chemically identical with thorium mesothorium- II with actinium the three B-members and radium- D with lead the three C-members and radium- E with bismuth thorium- D and actinium- D with thallium and radium- A with polonium.

, In the meantime, a systematic study of the chemical nature of those disintegration products not hitherto thoroughly studied from a chemical point of view had resulted in a remarkable extension of the feature which dominates the chemistry of the radio-elements.
RADIOACTIVE ELEMENT DEFINITION SERIES
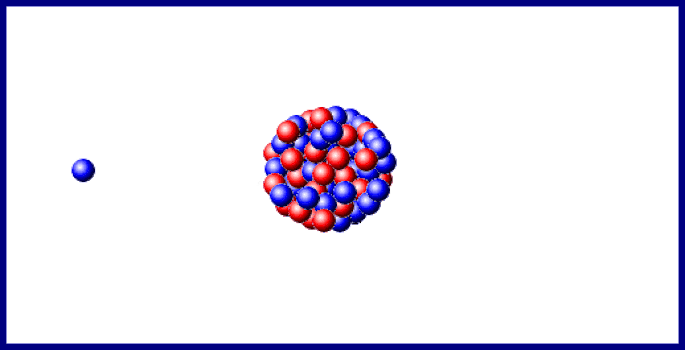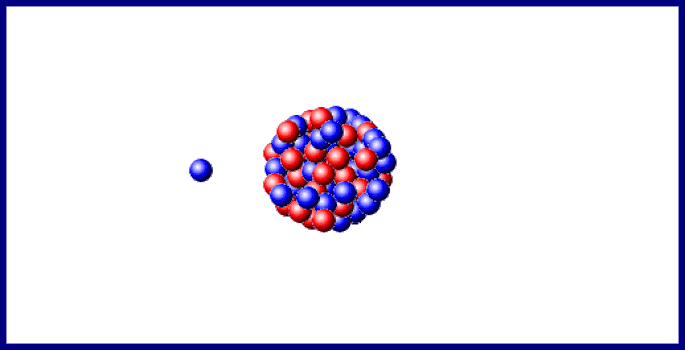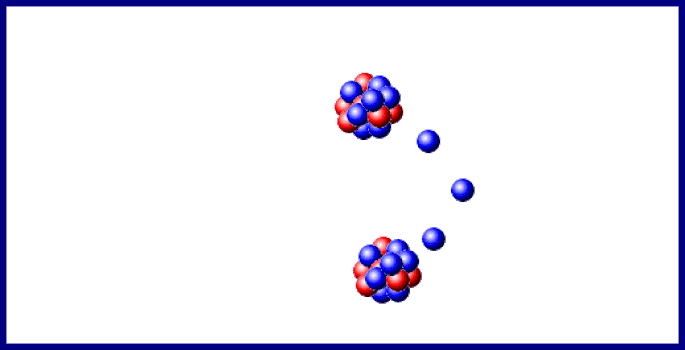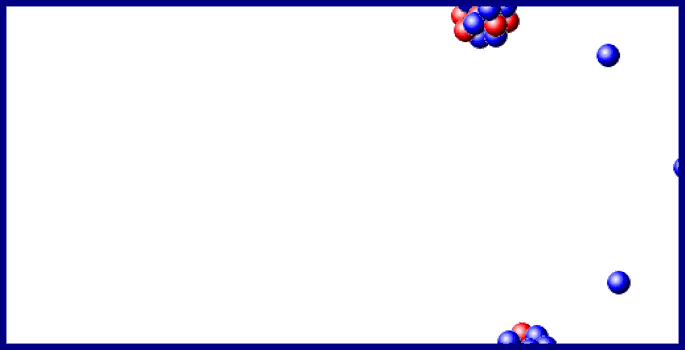
Last year doubtful points in the sequence of changes, consequent upon the branching of the disintegration series at the C-members, and on the existence, in uranium, of two chemically identical elements, uranium- I and - II, were cleared up, and the important step made that the B- and C-members of the three series exhibit identical electrochemical behaviour. In the last section of the 1910 Report, "Chemical Relationships of the Radio-elements," the existence of groups of radio-elements possessing identical chemical properties was shown to foreshadow "some embracing generalisation which will throw light, not only on radioactive processes, but on the elements in general and the Periodic Law." In 1911 the first step in this direction was made, when it was recognised that the expulsion of the α-particle causes the radio-element to change its position in the periodic table, not into the next family, but into the next but one in the direction of diminishing group number and diminishing atomic mass. The excerpt reproduced below describes isotopes and the displacement law.Įxcerpt from Chemical Society Annual Reports 10, 262-288 (1913) The arduous and futile work of attempting to separate by chemical means materials which clearly had different radioactive properties led to example after example of the phenomenon which was eventually recognized as isotopy. In his lecture at the award ceremony, he said of isotopes, "Put colloquially, their atoms have identical outsides but different insides." Atoms of the same element which are not identical in every particular represents a significant deviation from Dalton's concept of the atom ( chapter 7) however, the idea had surfaced from time to time before research on radioactive elements made their presence manifest. Soddy received the Nobel Prize for chemistry in 1921 for his work on isotopes. At about the same time, Soddy came to the conclusion that several substances with different radioactive properties and different atomic weights were chemically the same element. These rules taken together are known as the Displacement Law Kasimir Fajans published it slightly earlier than did Soddy. Emission of an α particle changes the emitting atom to an atom of the element two places to the left in the periodic table emission of a β particle changes the emitting atom to an atom of the element one place to the right. About 10 years later, he unravelled the rules for the elemental transformations which accompanied radioactive decay, first for α decay and later for β decay.
With Ernest Rutherford, he saw that radioactive substances were transformed from one element to another. Isotopes: Soddy Elements and Atoms: Chapter 20įrederick Soddy (1877-1956 see photo at Edgar Fahs Smith collection, University of Pennsylvania) is best known for three major contributions toward the understanding of radioactivity and associated phenomena.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
